Introduction
The ocean’s most fascinating and unique fish is the hogfish. It is a member of wrasse and can be found in both the western Atlantic Ocean (from North Carolina to South America) and in the eastern Gulf of Mexico (and the Caribbean Sea). The hogfish is a very popular fish for recreational and commercial fishing. It is well-known for its delicious flesh and unique appearance. This article will discuss the biology, habitats, diet, behavior, conservation status, and other aspects of the hogfish.
Biology
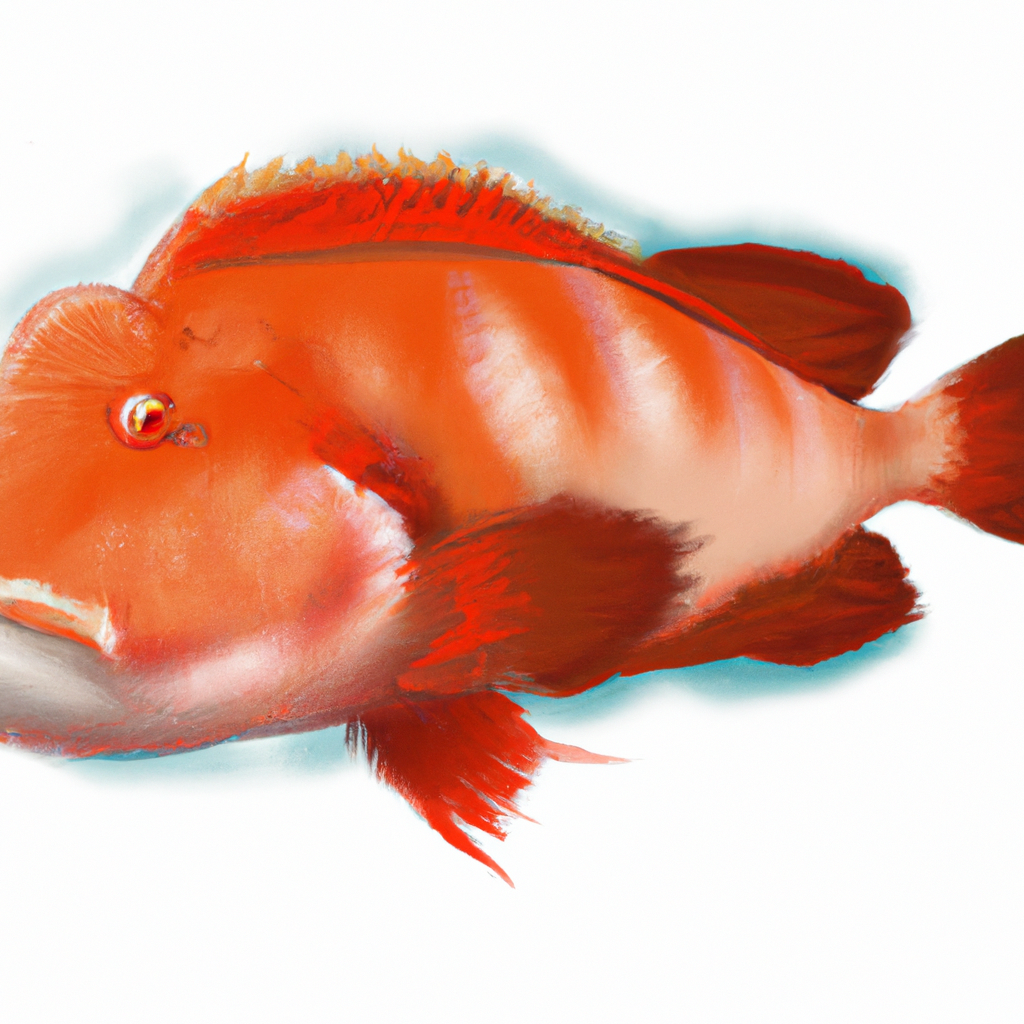
The hogfish, a medium-sized fish, can grow to up to 30 inches long and weigh up to 11 lbs. It has a long, slim body with a pointed nose that is used to dig in the sand for food. The hogfish is well-known for its bright, colorful appearance. It has a reddish brown body with white stripes radiating from its eyes. It has a distinctive “pig-like”, snout that gives it its name.
Anatomy
The unique anatomy of the hogfish makes it a very special species. It has a jaw structure that allows it small invertebrates to eat crustaceans. The fish uses its powerful jaws and teeth to crush and eat prey. The hogfish also has small teeth on its roof that it uses to crush hard-shelled prey. The large pelvic fins of the fish allow it to swim along the seafloor and forage.
Breeding
The hogfish is a hermaphrodite. This means it has both male- and female reproductive organs. The fish starts life as a female, and then becomes a male. The transition from male to female occurs around 2 to 3 years old. It can take up to a year for the process to complete. Once the fish is a male, it will release sperm into water to fertilize the eggs of its female counterpart.
Habitat
The hogfish can be found in many habitats, including wrecks, reefs, and artificial structures. It prefers sandy or rocky bottoms where it can hide behind rocks or coral. You can find the hogfish in seagrass beds where it feeds on small crustaceans and invertebrates.
Geographical Distribution
The hogfish can be found in the western Atlantic Ocean, North Carolina to South America, and in the eastern Gulf of Mexico as well as the Caribbean Sea. Bermuda is also home to the hogfish.
Migration
The hogfish is non-migratory, meaning it stays in the same area for most of its lives. It may, however, move to other areas in its range for food or mates.
Diet
The hogfish is an opportunistic eater, meaning it will eat any prey that is available. The hogfish eats small invertebrates such as shrimps, crabs, and worms. It also eats small fish, juvenile octopuses, and other small animals. The hogfish uses its strong sense of smell to find its prey.
Feeding Behavior
The hogfish is a bottom-dwelling fish. It uses its pointed, long snout to dig in the sand and find food. It uses its powerful jaws to crush hard-shelled prey like snails and crabs. Sometimes, the fish will follow larger fish or rays closely to eat the prey they have scouted from the sand.
Behavior
The hogfish is a solitary fish, but can be territorial during breeding season. The fish will defend its territory against other hogfish and similar species. The hogfish is also known for being curious and will often approach divers and snorkelers.
Activity
The hogfish is a diurnal fish, meaning it is active during daylight hours and sleeps at night. The hogfish spends most of its time searching for food on the bottom of the ocean floor.
Social Behavior
Although the hogfish is a single-species fish, it can form loose aggregations during mating or feeding. It is also known that the hogfish can change its color depending on its aggression level or mood.
Conservation Status
The hogfish is both a recreationally and commercially important fish. This has led to some areas being overfished. The South Atlantic Fishery Management Council issued new regulations in 2017 to protect the hogfish population. These regulations included a minimum size limit (16 inches) and a limit of one fish per person per night. Despite these regulations, some areas are still considered overfished.
Threats
There are many threats to the hogfish, including overfishing and habitat loss as well as climate change. The fish is also susceptible to pollution and other human activities, which can pollute water and degrade its habitat.
Conservation efforts
Fishing regulations, habitat restoration, education, and public education are some of the conservation efforts that aim to protect the hogfish population. These efforts aim to reduce the impact of human activity on the hogfish population, and ensure its long-term survival.
Conclusion
The hogfish is a fascinating and unique fish that is important to the ocean ecosystem. It is well-known for its distinctive appearance and delicious flesh. This fish is popular with recreational and commercial fishermen. The hogfish is vulnerable to overfishing and habitat destruction. We can help ensure the survival of this species by implementing conservation measures.